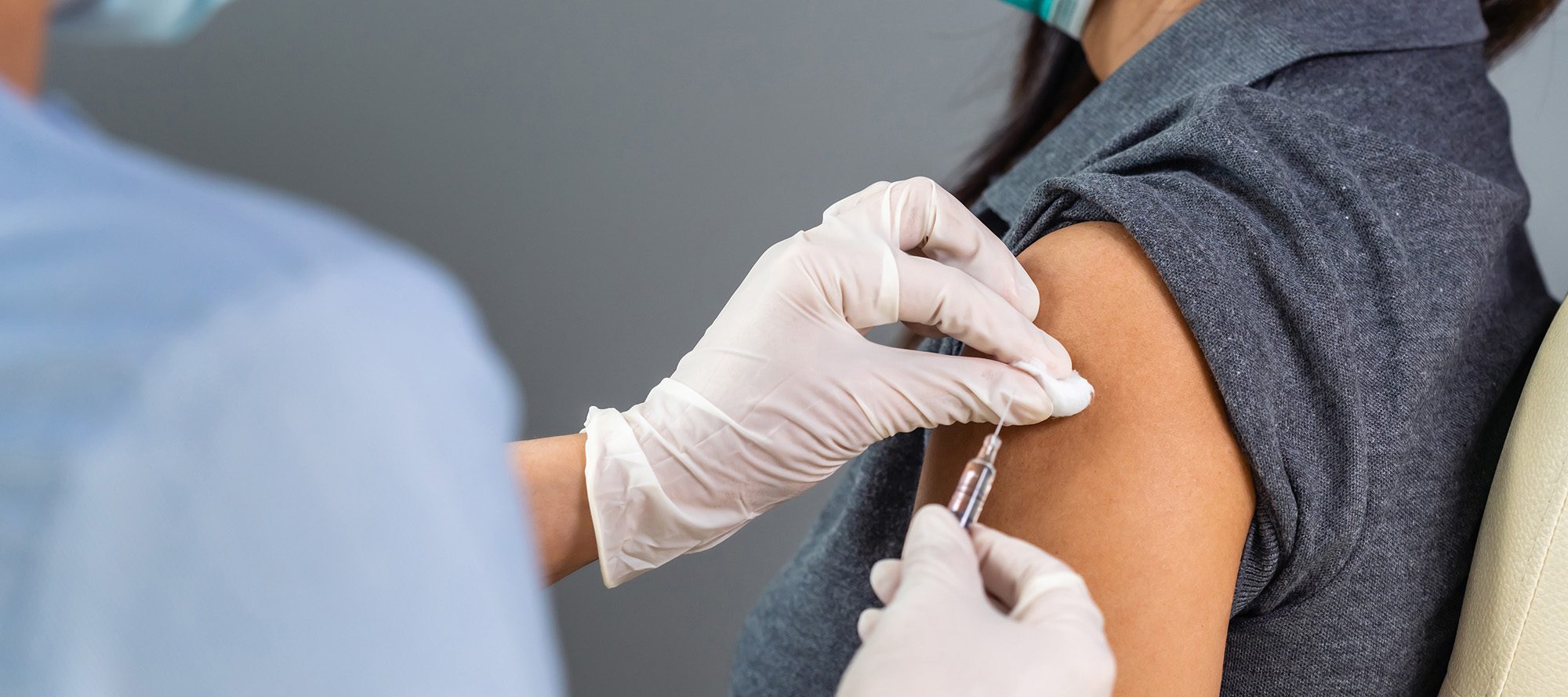
Estimated Effectiveness of Nirsevimab Against Respiratory Syncytial Virus
In this test-negative case-control study with 680 RSV test-positive cases and 2,410 RSV test-negative controls, nirsevimab’s estimated effectiveness was 68.4% against RSV infections, 80.5% against RSV-associated hospitalization, and 84.6% against severe RSV disease. Estimated effectiveness against RSV infection declined from 79.3% at 2 weeks postimmunization to 54.8% at 14 weeks postimmunization.
These are the results of a retrospective cohort study that used data from the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency and the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. They analyzed data from COVID-19 patients aged > 60 years from January to December 2022. The primary outcome was the occurrence of 27 PASCs within 30–120 days after COVID-19 diagnosis. Results: Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir significantly reduced the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure and cardiomyopathies (aHR, 0.86), cardiac dysrhythmias (aHR, 0.83), and ischemic stroke (aHR, 0.88). It also lowered the risk of hospitalization due to respiratory diseases including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (aHR, 0.92) and decreased renal disorders including dialysis needs (aHR, 0.57) and acute renal failure (aHR, 0.85). Molnupiravir reduced the risk of ischemic stroke (aHR, 0.84) and other cerebrovascular diseases (aHR, 0.84). Respiratory conditions decreased by approximately 13–14% (aHR, 0.87 and 0.86, respectively). Highlights: Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir significantly reduced the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Oral antivirals lowered the risk of hospitalization due to respiratory and renal diseases. Molnupiravir reduced ischemic stroke and other cerebrovascular disease risk. Respiratory conditions—COPD, asthma—decreased by approximately 13–14%.
Situation Dashboards

World Health Organization (WHO)

Johns Hopkins University (JHU)

COVID-19 in US and Canada