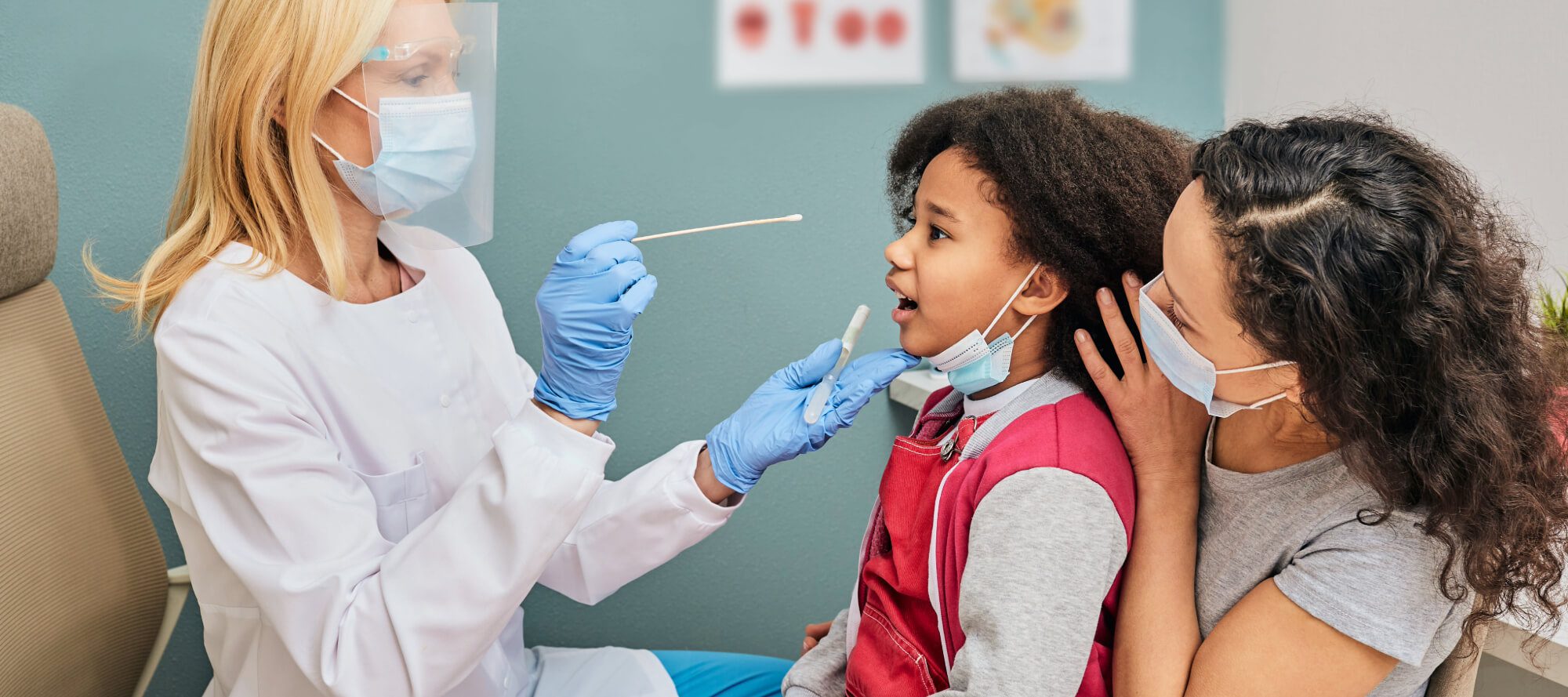
- Proton Pump Inhibitors and Risk of COVID-19 Infection in Children
These are the results of a retrospective, case-control study included all children < 21 years undergoing COVID-19 PCR testing at a tertiary children's hospital between March 2020 and January 2023. The main exposure was PPI usage. The primary outcome was COVID-19 infection. The secondary outcome was COVID-19 hospitalization. In total 116,209 patients age 8.5±6.2 years underwent 234,867 COVID-19 tests. Current PPI use was associated with a decreased risk of COVID-19 test positivity compared with PPI non-use [RR 0.85 (95% CI 0.76, 0.94), P = 0.002]; however, there was a significant interaction with time of testing, and an effect of PPIs was no longer seen in the final months of the study following lessening of COVID-19 precautions [RR 1.04 (95% CI 0.0.80, 1.36), P = 0.77]. PPI use was not associated with risk of hospitalization in patients positive for COVID-19 after adjusting for other hospitalization risk factors [RR 0.85 (95% CI 0.64, 1.13), P = 0.26]. The authors conclude by saying “We did not find an association between PPI use and increased COVID-19 susceptibility or severity in this pediatric sample.”
- Long Covid The Answers
This website launched July 5 is a credible, evidence-based destination for long haulers, carers and healthcare professionals to learn about Long COVID and find credible information and relief. It includes medically reviewed, evidence-based news; accredited Long COVID podcast for continued professional development; knowledgeable advisors; and an “Ask an Expert” section for answers to Long-COVID clinical questions.
Situation Dashboards

World Health Organization (WHO)
Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Situation from World Health Organization (WHO)

Johns Hopkins University (JHU)
Coronavirus COVID-19 Global Cases by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at JHU

COVID-19 in US and Canada
1Point3Acres Real-Time Coronavirus (COVID-19) Updates in US and Canada with Credible Sources

Genomic Epidemiology COVID-19
Genomic Epidemiology of (COVID-19) Maintained by the Nextstrain team, enabled by data from GISAID.