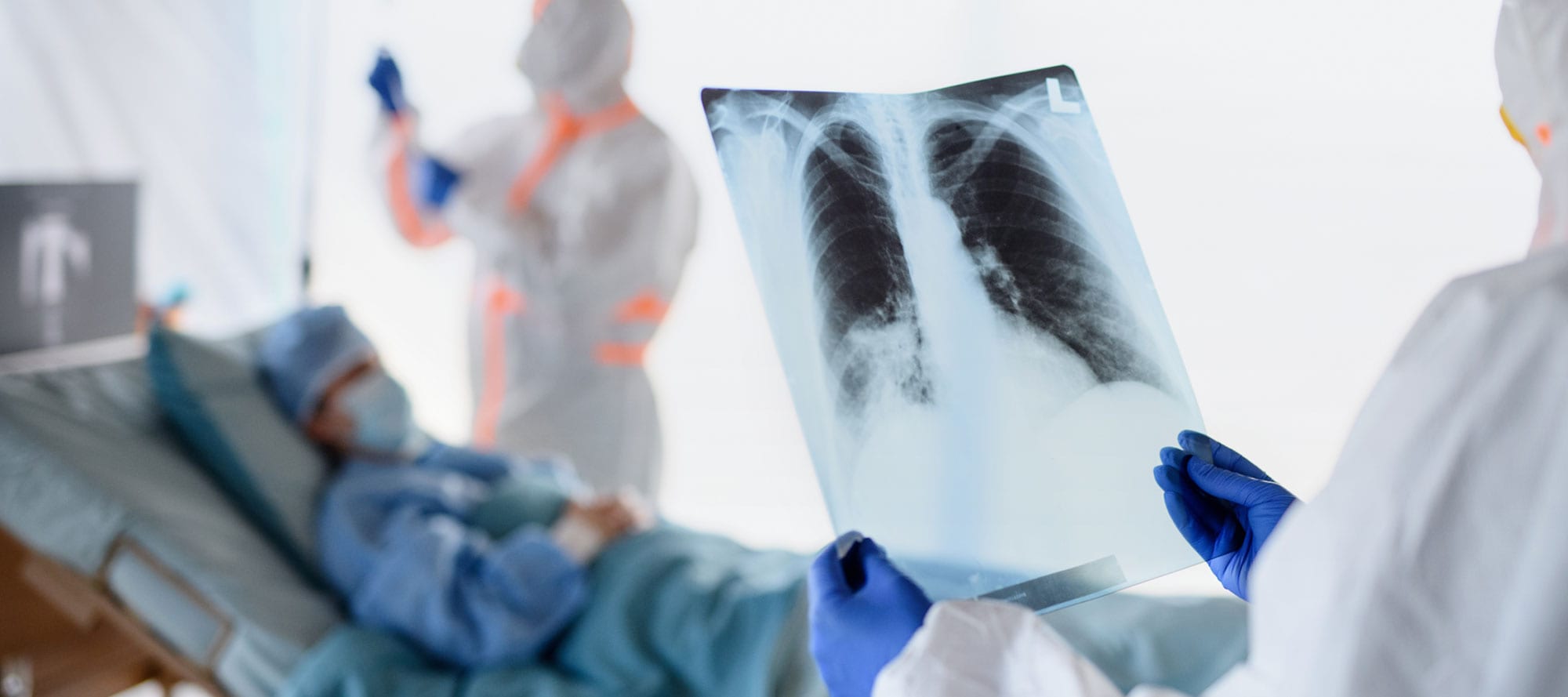
- Co-detection of respiratory pathogens in patients hospitalized with Coronavirus
A total of 183 adult patients testing positive by SARS CoV-2 RT-PCR on respiratory specimens were hospitalized with interstitial pneumonia at INCLIVA Health Research Institute, Valencia, Spain, of whom 103 were tested for other respiratory pathogens by a multiplexed PCR assay. despite the apparent rarity of coinfections in patients with Covid-19 pneumonia, routine testing for respiratory is advised, since agents for which specific therapy can be prescribed may be detected.
- Loss of smell and taste in combination with other symptoms is a strong predictor of COVID-19 infection
Loss of smell and taste were present in 59% of COVID-19 positive individuals throughout the UK compared to 18% of those negative to the test. A combination of loss of smell and taste, fever, persistent cough, fatigue, diarrhea, abdominal pain and loss of appetite is predictive of COVID-19 positive test. Results suggest that loss of taste and smell is a strong predictor of having been infected by the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
- Findings of acute pulmonary embolism in COVID-19 patients
This study retrospectively analyzed the results of COVID-19 patients who were admitted to out hospital and had undergone CTPA scans due to suspected APE and other clinical concerns. Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia are at risk of APE. When D-dimer remarkable increases, CTPA facilitates the diagnosis of APE and assesses its change during the course.
- Indoor transmission of SARS-CoV-2
Case reports were extracted from the local Municipal Health Commissions of 320 prefectural cities (municipalities) in China, not including Hubei province, between 4 January and 11 February 2020. All outbreaks involving three or more cases were identified the major characteristics of the enclosed spaces in which the outbreaks were reported were reviewed. All identified outbreaks of three or more cases occurred in an indoor environment, which confirms that sharing indoor space is a major SARS-CoV-2 infection risk.
Situation Dashboards



World Health Organization (WHO)
Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Situation from World Health Organization (WHO)


Johns Hopkins University (JHU)
Coronavirus COVID-19 Global Cases by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at JHU


COVID-19 in US and Canada
1Point3Acres Real-Time Coronavirus (COVID-19) Updates in US and Canada with Credible Sources


Genomic Epidemiology COVID-19
Genomic Epidemiology of (COVID-19) Maintained by the Nextstrain team, enabled by data from GISAID.